VDSL -
ADSL -
G.hs(HandShake) -
Japan xDSL -
Webmaster & EDH
For the last few years, I have been involved with developing technology and
standards for xDSL. xDSL provides very high speed access to the internet
for homes and business. An overview article on xDSL standards:
Report on Global xDSL Standards from the ITU
appeared in the December 1998 issue of The Telechoice Report on xDSL.

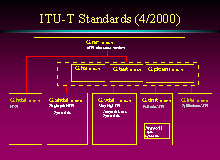
Click for larger image; use browser "Back" to return
There are two standards for ADSL: G.dmt (G.992.1) and G.lite (G.992.2). G.dmt provides access
speeds of several megabit/sec. G.lite provides access at about one megabit/sec and is
consumer installable.
- G.992.1 (G.dmt) editor
Title: Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) Transceiver
Recommendation G.992.1 describes Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line
(ADSL) Transceivers on a metallic twisted pair that allows high speed
data transmission between the network operator end (ATU-C) and the
customer end (ATU-R). Recommendation G.992.1 provides a variety of
bearer channels in conjunction with one of three other services
dependent on the environment: 1) ADSL transmission simultaneously on the
same pair with voice (band) service, 2) ADSL transmission simultaneously
on the same pair with G.961 (Appendix I or II) ISDN services, or 3) ADSL
transmission on the same pair with voice-band transmission and with
TCM-ISDN (G.961 Appendix III) in an adjcent pair. Systems allow
approximately 6 Mbit/s downstream and approximately 640 kbit/s upstream
data rates depending on the deployment and noise environment.
G.994.1 is the common handshaking or activation procedure for ITU-T xDSL
modems. It is fully interoperable with the activation procedures for
legacy DSL modems but offers several benefits for service providers:
robustness, exchange of capabilities information, notification of the
application and service requests, backwards and forwards compatibility
for other DSL modem standards.
Higher layers on each end of the DSL modems can indicate
service and application requirements during the handshake so that the
appropriate DSL Recommendation from the family of DSL Recommendations
will be activated following the G.994.1 handshake. This allows
providers to flexibly tailor the service bandwidth and latency
requirements of the customer's dynamic applications and environments
including mobile DSL modems or modem pooling.
Contributions developing G.hs
Contributions developing next generation G.hs and xDSL intialization
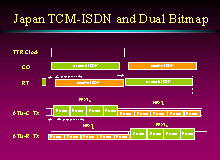
Japan's unique TCM-ISDN ping pong modulation can cause particularly
strong cross talk interference into xDSL systems. Several Japanese
companies developed the Dual Bit Map (DBM) technique that
synchronizes xDSL transmission with the TCM-ISDN transmission in adjacent pairs
giving xDSL in Japan the same performance as other regions. The companies
received the Nikkei 1999 Technology Award for the DBM technology incorporated
into Annex C of G.lite and G.dmt.
I have promoted the use of Electronic Document Handling (EDH) in
Q4/15 by designing an integrated system based on PERL scripts that:
- create an clickable HTML index of all documents at a meeting
(Example)
- A web-based request for contribution document numbers (Example)
that emails the assigned document number and a MS Word file
that is a skeleton of the contribution with the basic information
already inserted.
- A web-based contribution upload mechanism with automatic
email notification to the Q4/15 mailing list. (Example)
- A copy of the Q4/15 homepage
- EDH guidelines